Azure SQL Database Instance Pools
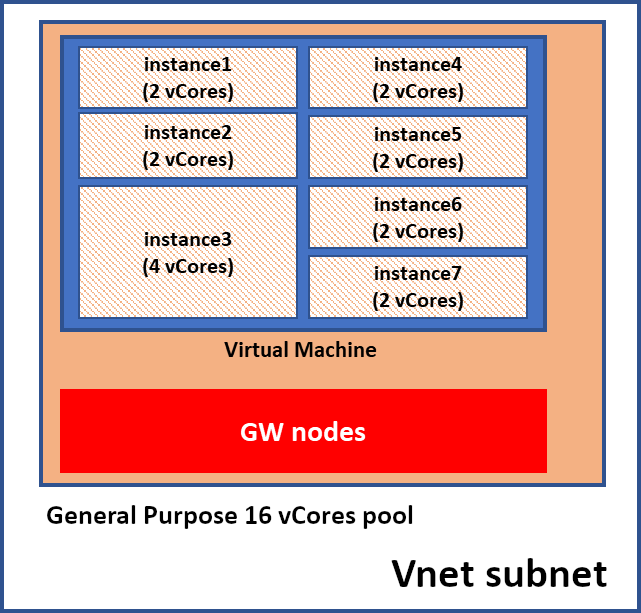
Instance pools allow you to pre-provision compute resources according to your total migration requirements. You can then deploy several individual managed instances up to your pre-provisioned compute level. For example, if you pre-provision 8 vCores, you can deploy two 2 vCore and one 4 vCore instances, and then migrate the database to these instances. For example, smaller and less compute-intensive workloads often have to be consolidated into a larger managed instance when migrating to the cloud, before the pool becomes available. The need to migrate groups of databases to a larger instance typically requires careful capacity planning and resource governance, additional security considerations, and some additional data consolidation work at the instance level.
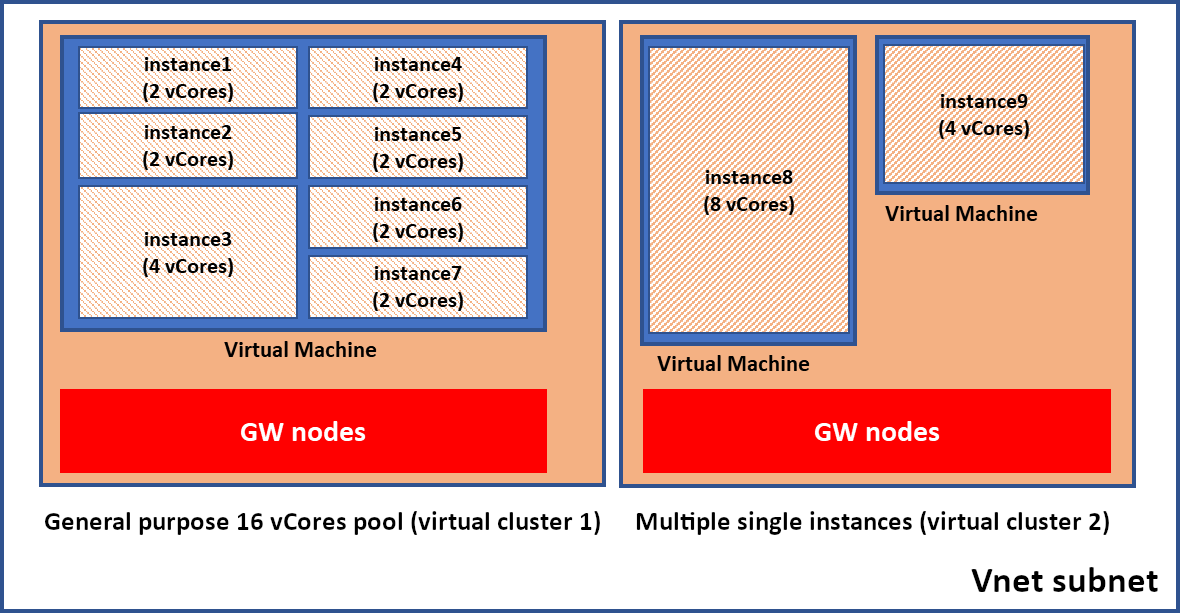
In addition, instance pools support native VNet integration so that you can deploy multiple instance pools and multiple single instances in a single subnet.
Instance pools provide the following benefits:
- Ability to host vCore instances. * For example only in the instance pool.
- Predictable and fast instance deployment time (up to 5 minutes).
- Minimum IP address allocation.
The following diagram shows an example pool in which multiple instances are deployed in a virtual network subnet.
Instance pools enable deployment of multiple instances on the same virtual machine where the size of the virtual machine's count is based on the total number of vCores allocated to the pool. This architecture allows virtual machines to be divided into multiple instances, which can be of any supported size, including 2 vCores (2 vCore instances are available only for instances in pools).
Once the pool is started, management on the instance in the pool is more rapid. These operations are fast because the deployment or expansion of a virtual cluster (dedicated to a virtual machine) is not part of providing a managed instance.
Design of Case Pools
Occasion pools have comparative design to standard overseen examples (single cases). To help arrangements inside Azure Virtual Networks (VNets) and to give seclusion and security to clients, example pools likewise depend on virtual groups. Virtual groups speak to a committed arrangement of disconnected virtual machines sent inside the client's virtual system subnet.
The fundamental distinction between the two organization models is that example pools permit different SQL Server process arrangements on the equivalent virtual machine hub, which are asset represented utilizing Windows Job Objects, while single occurrences are in every case alone on a virtual machine hub.
Design of Case Pools
Occasion pools have comparative design to standard overseen examples (single cases). To help arrangements inside Azure Virtual Networks (VNets) and to give seclusion and security to clients, example pools likewise depend on virtual groups. Virtual groups speak to a committed arrangement of disconnected virtual machines sent inside the client's virtual system subnet.
The fundamental distinction between the two organization models is that example pools permit different SQL Server process arrangements on the equivalent virtual machine hub, which are asset represented utilizing Windows Job Objects, while single occurrences are in every case alone on a virtual machine hub.
Each occasion pool makes a different virtual bunch underneath. Examples inside a pool and single occasions sent in the equivalent subnet don't share figure assets assigned to SQL Server procedures and entryway parts, this guarantees execution consistency. Get instant dial (+1-800-201-4243) our Microsoft support phone number. We are always available for your help.
More info: http://bit.ly/2Kkiw5a
Or
Call Now: +1-800-201-4243


Comments
Post a Comment